1. A 5000-kg car accelerated from rest to 20 m/s. Determine the net work done on the car.
Known :
Mass (m) = 5000 kg
Initial speed (vo) = 0 m/s (car rest)
Final speed (vt) = 20 m/s
Wanted : net work
Solution :
The work-kinetic energy principle :
Wnet = ΔEK
Wnet = ½ m (vt2 – vo2)
Wnet = net work
ΔEK = the change in kinetik energy
m = mass (kg),
vt = final speed (m/s),
vo = initial speed (m/s).
Net work :
Wnet = ½ m (vt2 – vo2)
Wnet = ½ (5000)(202 – 02)
Wnet = (2500)(400 – 0)
Wnet = (2500)(400)
Wnet = 1000,000 Joule
2. A 10-kg object accelerated from 5 m/s to 10 m/s. Determine the net work done on the object!
Known :
Mass (m) = 10 kg
Initial speed (vo) = 5 m/s
Final speed (vt) = 10 m/s
Wanted : net work
Solution :
Net work :
Wnet = ΔEK
Wnet = ½ m (vt2 – vo2)
Wnet = ½ (10)(102 – 52)
Wnet = (5)(100 – 25)
Wnet = (5)(75)
Wnet = 375 Joule
3. A 2000-kg car decelerated from 10 m/s to 5 m/s. What is the work done on the car ?
Known :
Car’s mass (m) = 2000 kg
Initial speed (vo) = 10 m/s
Final speed (vt) = 5 m/s
Wanted: net work
Solution :
Net work :
Wnet = ΔEK
Wnet = ½ m (vt2 – vo2)
Wnet = ½ (2000)(52 – 102)
Wnet = (1000)(25 – 100)
Wnet = (1000)(-75)
Wnet = -75,000 Joule
The minus sign indicates that the direction of displacement is opposite with the direction of the net force.
4. A 60-N constant force exerted on a 10-kg object for 12 seconds. The initial velocity of an object is 6 m/s and the direction of the object is the same as the direction of the force.
(1) Work done on the object is 30,240 Joule
(2) The final kinetic energy is 30,240 joule
(3) Power is 2,520 Watt
(4) Th increase in the kinetic energy of the object is 180 Joule
The correct statements are…
Known :
Force (F) = 60 N
Time interval (t) = 12 seconds
Mass of object (m) = 10 kg
Initial velocity (vo) = 6 m/s
Wanted : The correct statements
Solution :
Acceleration of object :
∑F = m a
60 = 10 a
a = 60 / 10 = 6 m/s2
The final velocity :
vt = vo + a t
vt = 6 + (6)(12)
vt = 6 + 72
vt = 78 m/s
The distance traveled in 12 seconds :
s = vo t + 1/2 a t2
s = (6)(12) + 1/2 (6)(12)2
s = 72 + (3)(144)
s = 72 + 432
s = 504 meters
(1) Work done by force
W = F s = (60)(504) = 30,240 Joule
(2) The final kinetic energy
KE = 1/2 m vt2 = 1/2 (10)(78)2 = (5)(6084) = 30,420 Joule
(3) Power
P = W / t = 30,240 / 12 = 2,520 Joule/second
(4) The increase in the kinetic energy
ΔKE = 1/2 m vt2 – 1/2 m vo2 = 1/2 m (vt2 – vo2) = 1/2 (10)(782 – 62) = 5 (6084 –36) = 5 (6048)
ΔKE = 30,240 Joule
5. The larger work is done by object number…
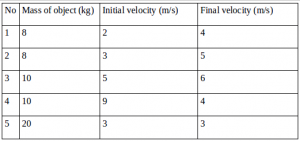
Solution :
Net work = change of th kinetic energy
Wnet = ½ m (vt2 – vo2)
The larger work :
W1 = ½ (8)(42 – 22) = (4)(16 – 4) = (4)(12) = 48 Joule
W2 = ½ (8)(52 –32) = (4)(25 – 9) = (4)(16) = 64 Joule
W3 = ½ (10)(62 – 52) = (5)(36 – 25) = (5)(11) = 55 Joule
W4 = ½ (10)(42 – 02) = (5)(16 – 0) = (5)(16) = 80 Joule
W5 = ½ (20)(32 – 32) = (10)(9 – 9) = (10)(0) = 0 Joule
6. A 4000-kg car travels along straight line at 25 m/s. The car is decelerated so that the car’s final velocity is 15 m/s. What is the work done on the car.
Known :
Mass (m) = 4000 kg
The initial velocity (vo) = 25 m/s
The final velocity (vt) = 15 m/s
Wanted : Work done on car
Solution :
Wnet = ½ m (vt2 – vo2) = ½(4000)(152-252) = (2000)(225-625) = (2000)(-400) = -800,000 Joule = -800 kJ
7. A 0.1-kg thrown horizontally at 6 m/s from the height of 5 meters. If the acceleration of gravity is 10 m/s2, then what is the kinetic energy of ball at the height of 2 meters.
Known :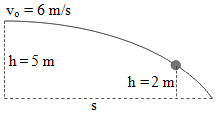
Mass (m) = 0.1 kg
The change in height (h) = 5 m – 2 m = 3 meters
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m/s2
Wanted : The kinetic energy at the height of 2 meters.
Solution :
Projectile motion can be understood by analyzing the horizontal and vertical components of the motion separately. Motion in horizontal direction analyzed as the constant velocity motion and motion in vertical direction analyzed as free fall motion or vertical motion.
The initial mechanical energy = the gravitational potential energy.
PE = m g h = (0.1)(10)(3) = 3 Joule.
The final mechanical energy = the kinetic energy.
KE = 3 Joule.
8. A 1000-kg car accelerated from rest and travels at 5 m/s. What is the work done by car?
Known :
Mass (m) = 1000 kg
Initial velocity (vo) = 0
Final velocity (vt) = 5 m/s
Wanted : Work (W) done by car
Solution :
Wnet = ½ m (vt2 – vo2)
Work done by car :
Wnet = ½ (1000)(52 – 02) = (500)(25 – 0) = (500)(25) = 12,500 Joule
9. A 500-gram ball thrown vertical upward from the surface of earth with the initial velocity 10 m/s2. Acceleration due to gravity is 10 ms-2. What is th work done by the weight force when ball reaches the maximum height.
Known :
Mass of ball (m) = 500 gram = 0.5 kg
Initial velocity (vo) = 10 m/s2
Final velocity (vt) = 0 (velocity at the highest point)
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m/s2
Wanted : Work (W) don by weight
Solution :
The net work done by net force on an object = the change in the kinetic energy.
Wnet = ΔEK = EKt – EKo
Wnet = ½ m vt2 – ½ m vo2 = ½ m (vt2 – vo2)
KEt = the final kinetic energy, KEo = the initial kinetic energy, m = mass of object, vt = the final velocity of object, vo = initial velocity of object.
Net work :
Wnet = ½ m (vt2 – vo2) = ½ (0.5)(02 – 102)
Wnet = (0.25)(-100) = -25 Joule
Minus sign indicates that the direction of displacement is opposite to the weight of the ball. The direction of ball is upright and the direction of weight is downright.
10. A 1-kg object free fall with the height difference = 2.5 meters. Acceleration due to gravity is 10 m.s-2. What is the work done on the object?
Known :
Mass of ball (m) = 1 kg
Initial velocity (vo) = 0 m/s
Height (h) = 2.5 meters
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m/s2
Wanted : Net work during displacement
Solution :
Final velocity of ball (vt)
Calculated using the equation of free fall motion. Known : Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m/s2, The change in height of ball (h) = 2.5 meters. Wanted : Final velocity.
vt2 = 2 g h = 2(10)(2.5) = 2(25)
vt = √2(25)
vt = 5√2
Net work = the change in kinetic energy
Wnet = ΔEK = ½ m (vt2 – vo2) = ½ (1){(5√2)2 – 02}
Wnet = ½ (25)(2) = 25 Joule
11. A 2-kg object travels at 72 km/hour. After travels 400 meters, the final velocity of object is 144 km/hour. Acceleration due to gravity is 10 ms-2. Find the net work.
Known :
Mass of object (m) = 2 kg
Initial velocity (vo) = 72 km/jam = 20 m/s
Final velocity (vt) = 144 km/jam = 40 m/s
Distance (s) = 400 meters
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m/s2
Wanted : The net work
Solution :
The net work = changes of the kinetic energy
Wnet = ΔEK = ½ m (vt2 – vo2) = ½ (2)(402 – 202}
Wnet = ½ (2)(1600 – 400) = 1200 Joule
12. A 2-kg object travels at 2 ms–1. The work done ob the object is 21 Joule. What is the final velocity of object.
Known :
Mass (m) = 2 kg
Initial velocity (vo) = 2 m/s
Work (W) = 21 Joule
Wanted : final velocity (vt)
Solution :
Wnet= ΔEK
Wnet= 1/2 m vt2 -1/2 m vo2
Wnet = 1/2 m (vt2 – vo2)
21 = 1/2 (2) (vt2 – 22)
21 = (vt2 – 22)
21 = vt2 – 4
vt2 = 21 + 4 = 25
vt = √25
vt = 5 m/s
13. A 8 N constant force acts on an object with mass of 16 kg. If the object initially at rest, then determine the speed of the object after force acts on the object for 4 seconds.
Known :
Constant force (F) = 8 Newton
Mass of object (m) = 16 kg
Initial speed of object (vo) = 0 m/s
Time interval force acts on object (t) = 4 seconds
Wanted : The final speed (vt)
Solution :
Work = The change in the kinetic energy
W = KE final – KE initial
W = ½ m vt2 – ½ m vo2
W = ½ m vt2 – 0
W = ½ m vt2 —— Equation 1
Work = Force x Displacement
W = F d
W = 8 d
Use the equation of nonuniform linear motion below to calculate displacement (d) :
d = vo t + ½ a t2
d = displacement, vo = initial velocity, t = time interval, a = acceleration
d = 0 + ½ a t2 = ½ a t2 —-> a = (vt – vo) / t = vt / t
d = ½ (vt / t) t2
d = ½ (vt) t
Change displacement (d) on equation of Work with displacement (d) in this equation :
W = 8 d
W = 8(1/2)(vt)(t)
W = (4)(vt)(t) —— equation 2
Equation 1 = Equation 2
W = W
½ m vt2 = (4)(vt)(t)
½ m vt = (4)(t)
½ (16)(vt) = 4(4)
8 vt = 16
vt = 16 / 8
vt = 2 meters/second
14. To increase the speed of an object become 2 times of the initial speed, determine work required in the process…
Known :
Mass of object (m) = 1 kg
Initial speed (vo) = 1 m/s
Final speed (vt) = 2 x initial speed = 2 x 1 = 2 m/s
Wanted : Work
Solution :
The initial kinetic energy :
KE initial = ½ m vo2 = ½ (1)(1)2 = ½ (1)(1) = ½ (1) = 0.5
The final kinetic energy when the speed of object becomes 2 time of its initial speed :
KE final = ½ m vt2 = ½ (1)(2)2 = ½ (4) = 2
Theorem of work-kinetic energy :
Work = The change in kinetic energy
Work = The final kinetic energy– the initial kinetic energy
Work = 2 – 0.5
Work = 1.5
The initial kinetic energy = 0.5
Work = 3 x 0.5 = 1.5
Required work 3 times of its initial kinetic energy.
15. A car with mass of 1500 kg moves with speed of 36 km/hour on a linear and smooth horizontal road. The car accelerated to 72 km/hour. Determine the work required to acceleration the car.
Known :
Mass of car (m) = 1500 kg
Initial speed of car (vo) = 36 km/hour = 36,000 meters / 3600 second = 10 meters/second
Final speed of car (vt) = 72 km/hour = 72,000 meters / 3600 second = 20 meters/second
Wanted : Work required to accelerates the car
Solution :
Theorem of work-kinetic energy :
W = EK final – EK initial
W = ½ m vt2 – ½ m vo2 = ½ m (vt2 –vo2)
W = ½ (1500)(202 – 102)
W = ½ (1500)(400 – 100)
W = ½ (1500)(300)
W = (1500)(150)
W =225,000 Joule
16. An object with mass of 2 kg initially moves at speed of 72 km.hour-1. After move in horizontal straight road as far as 400 m, the speed of the object is 144 km.hour-1. Determine the total work on the object.
Known :
Mass of object (m) = 2 kg
Initial speed (vo) = 72 km/hour = 72,000 meters / 3600 second = 20 m/s
Final speed (vt) = 144 km/hour = 144,000 meters / 3600 second = 40 m/s
Displacement of object = 400 meters
Wanted : Net work on the object
Solution :
Theorem of work-kinetic energy states that the net work acts on an object same as the change of the kinetic energy of the object.
W net = KE final – KE initial
W net = ½ m vt2 – ½ m vo2
W net = ½ m (vt2 – vo2)
W net = ½ (2)(402 – 202)
W net = 1600 – 400
W net = 1200 Joule
Description :
W = Work, KE = kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
17. A 10-gram bullet moving at a constant 100 m/s. What is the kinetic energy of the bullet.
Known :
Mass of bullet (m) = 10 gram = 10/1000 kilogram = 1/100 kilogram = 0.01 kilogram
Bullet’s speed (v) = 100 meters/second
Wanted: Kinetic energy
Solution :
KE = 1/2 m v2
KE = 1/2 (0,01 kg)(100 m/s)2
KE = 1/2 (0,01 kg)(10.000 m2/s2)
KE = (0,01 kg)(5000 m2/s2)
KE = 50 kg m2/s2
KE = 50 Joule
[wpdm_package id=’1191′]
- Work done by force problems and solutions
- Work-kinetic energy problems and solutions
- Work-mechanical energy principle problems and solutions
- Gravitational potential energy problems and solutions
- Potential energy of elastic spring problems and solutions
- Power problems and solutions
- Application of conservation of mechanical energy for free fall motion
- Application of conservation of mechanical energy for up and down motion in free fall motion
- Application of conservation of mechanical energy for motion on a curve surface
- Application of conservation of mechanical energy for motion on an inclined plane
- Application of conservation of mechanical energy for projectile motion
