1. If R1 = 2 Ω, R2 = 4 Ω, R3 = 6 Ω, determine the electric current flows in the circuit below.
Known :
Resistor 1 (R1) = 2 Ω 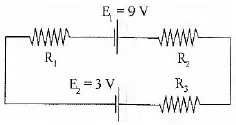
Resistor 2 (R2) = 4 Ω
Resistor 3 (R3) = 6 Ω
Source of emf 1 (E1) = 9 V
Source of emf 2 (E2) = 3 V
Wanted: Electric current (I)
Solution :
This question relates to Kirchhoff’s law. How to solve this problem:
First, choose the direction of the current. You can decide the opposite current or direction in the clockwise direction.
Second, when the current through the resistor (R) there is a potential decrease so that V = IR signed negative. Third, if the current moves from low to high voltage (- to +) then the source of emf (E) signed positive because of the charging of energy at the emf source. If the current moves from high to low voltage (+ to -) then the source of emf (E) signed negative because of the emptying of energy at the emf source.
In this solution, the direction of the current is the same as the direction of clockwise rotation.
– I R1 + E1 – I R2 – I R3 – E2 = 0
– 2 I + 9 – 4 I – 6 I – 3 = 0
– 12 I + 6 = 0
– 12 I = – 6
I = -6 / -12
I = 0.5
The electric current flows in the circuit are 0.5 A. The electric current signed positive means that the direction of the electric current is the same as the direction of clockwise rotation. If the electric current is negative, then the electric current is opposite the clockwise direction.
2. Determine the electric current that flows in the circuit as shown in the figure below.
Solution :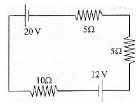
In this solution, the direction of the current is the same as the direction of clockwise rotation.
-20 – 5I -5I – 12 – 10I = 0
-32 – 20I = 0
-32 = 20I
I = -32 / 20
I = -1.6 A
Because the electric current is negative, the direction of the electric current is actually opposite to the clockwise direction. The direction of electric current is not the same as estimation.
3. Determine the electric current that flows in the circuit as shown in the figure below.
Solution :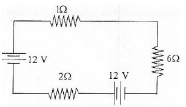
In this solution, the direction of current is the same as the direction of clockwise rotation.
– I – 6I + 12 – 2I + 12 = 0
-9I + 24 = 0
-9I = -24
I = 24 / 9
I = 8 / 3 A
4. An electric circuit consists of four resistors, R1 = 12 Ohm, R2 = 12 Ohm, R3 = 3 Ohm and R4 = 6 Ohm, are connected with source of emf E1 = 6 Volt, E2 = 12 Volt. Determine the electric current flows in the circuit as shown in figure below.
Known :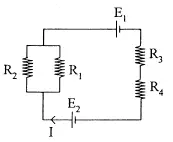
Resistor 1 (R1) = 12 Ω
Resistor 2 (R2) = 12 Ω
Resistor 3 (R3) = 3 Ω
Resistor 4 (R4) = 6 Ω
Source of emf 1 (E1) = 6 Volt
Source of emf 2 (E2) = 12 Volt
Wanted : The electric current flows in the circuit (I)
Solution :
Resistor 1 (R1) and resistor 2 (R2) are connected in parallel. The equivalent resistor :
1/R12 = 1/R1 + 1/R2 = 1/12 + 1/12 = 2/12
R12 = 12/2 = 6 Ω
In this solution, the direction of current is the same as the direction of clockwise rotation.
– I R12 – E1 – I R3 – I R4 + E2 = 0
– 6 I – 6 – 3I – 6I + 12 = 0
– 6I – 3I – 6I = 6 -12
– 15I = – 6
I = -6/-15
I = 2/5 A
5. Determine the electric current that flows in circuit as shown in figure below.
Known :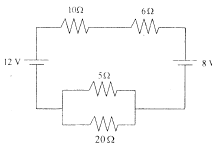
Resistor 1 (R1) = 10 Ω
Resistor 2 (R2) = 6 Ω
Resistor 3 (R3) = 5 Ω
Resistor 4 (R4) = 20 Ω
Source of emf 1 (E1) = 8 Volt
Source of emf 2 (E2) = 12 Volt
Wanted : The electric current that flows in circuit
Solution :
Resistor 3 (R3) and resistor 4 (R4) are connected in parallel. The equivalent resistor :
1/R34 = 1/R3 + 1/R4 = 1/5 + 1/20 = 4/20 + 1/20 = 5/20
R34 = 20/5 = 4 Ω
In this solution, the direction of current is the same as the direction of clockwise rotation.
– I R1 – I R2 – E1 – I R34 + E2 = 0
– 10I – 6I – 8 – 4I + 12 = 0
– 10I – 6I – 4I = 8 – 12
– 20I = – 4
I = -4/-20
I = 1/5 A
I = 0.2 A
6. Determine the electric current that flows in circuit as shown in figure below.
Known :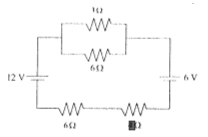
Resistor 1 (R1) = 1 Ω
Resistor 2 (R2) = 6 Ω
Resistor 3 (R3) = 6 Ω
Resistor 4 (R4) = 4 Ω
Source of emf 1 (E1) = 12 Volt
Source of emf 2 (E2) = 6 Volt
Wanted : The electric current that flows in circuit
Solution :
Resistor 1 (R1) and resistor 2 (R2) are connected in parallel. The equivalent resistor :
1/R12 = 1/R1 + 1/R2 = 1/1 + 1/6 = 6/6 + 1/6 = 7/6
R12 = 6/7 Ω
The direction of current is the same as the direction of clockwise rotation.
E1 – I R12 – E2 – I R4 – I R3 = 0
12 – (6/7)I – 6 – 4I – 6I = 0
12 – 6 – (6/7)I – 4I – 6I = 0
6 – (6/7)I – 10I = 0
6 = (6/7)I + 10I
6 = (6/7)I + (70/7)I
6 = (76/7)I
(6)(7) = 76I
42 = 76I
I = 42/76
I = 0.5 A
