1. Ideal gases in a closed container initially have volume V and pressure P. If the final pressure is 4P and the volume is kept constant, what is the ratio of the initial kinetic energy with the final kinetic energy.
Known :
Initial pressure (P1) = P
Final pressure (P2) = 4P
Initial volume (V1) = V
Final volume (V2) = V
Wanted: The ratio of the initial kinetic energy with the final kinetic energy (KE1 : KE2)
Solution :
The relation between pressure (P), volume (V) and kinetic energy (KE) of ideal gases :
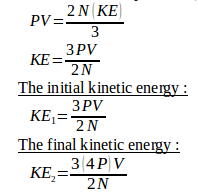
The ratio of the initial kinetic energy with the final kinetic energy :
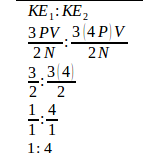
2. What is the average translational kinetic energy of molecules in an ideal gas at 57oC.
Known :
Temperature of gas (T) = 57oC + 273 = 330 Kelvin
Boltzmann‘s constant (k) = 1.38 x 10-23 Joule/Kelvin
Wanted: The average translational kinetic energy
Solution :
The relation between kinetic energy (KE) and the temperature of the gas (T) :
![]()
The average translational kinetic energy :
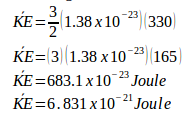
3. A gas at 27oC in a closed container. If the kinetic energy of the gas increases 2 times the initial kinetic energy, thus the final temperature of the gas is…
Known :
Initial temperature (T1) = 27oC + 273 = 300 K
Initial kinetic energy = KE
Final kinetic energy = 4 KE
Wanted: The final temperature (T2)
Solution :

4. An ideal gas is in a closed container, is heated so that the final average velocity of particles of gas increases by 3 times the initial average velocity. If the initial gas temperature is 27oC, then the final temperature of the ideal gas is…
Known :
Initial temperature = 27oC + 273 = 300 Kelvin
Initial velocity = v
Final velocity = 2v
Wanted : The final temperature of ideal gas
Solution :
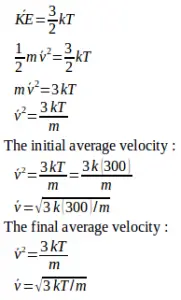
The final average velocity = 2 x the initial average velocity
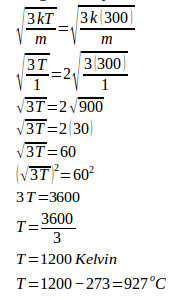
5. Three moles of gas are in a 36 liters volume space. Each gas molecule has a kinetic energy of 5 x 10-21 Joule. Universal gas constant = 8.315 J/mole.K and Boltzmann’s constant = 1.38 x 10-23 J/K. What is the gas pressure in the container.
Known :
Number of moles (n) = 3 moles
Volume = 36 liters = 36 dm3 = 36 x 10-3 m3
Boltzmann’s constant (k) = 1.38 x 10-23 J/K
Kinetic energy (KE) = 5 x 10–21 Joule
Universal gas constant (R) = 8.315 J/mole.K
Wanted : Gas pressure (P)
Solution :
Calculate the temperature using the equation of kinetic energy of gas.
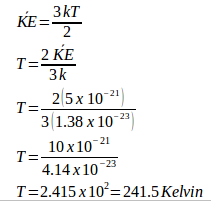
Calculate the gas pressure using th equation of ideal gas law (in number of moles, n) :
P V = n R T
P (36 x 10-3) = (3)(8.315)(241.5)
P (36 x 10-3) = 6024.22
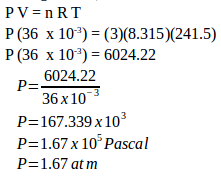
The gas pressure is 1.67 x 105 Pascal or 1.67 atmospheres.
