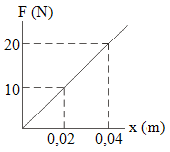
1. A graph of force (F) versus elongation (x) shown in the figure below. Find the spring constant!
 Solution
Solution
Hooke’s law formula :
k = F / x
F = force (Newton)
k = spring constant (Newton/meter)
x = the change in length (meter)
Spring constant :
k = 10 / 0.02 = 20 / 0.04
k = 500 N/m
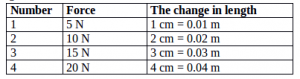
2. Determine the spring constant.
Solution
Spring constant :
k = F / x
k = 5 / 0.01 = 10 / 0.02 = 15 / 0.03 = 20 / 0.04
k = 500 N/m
3. Spring A has the original length of 60 cm and spring B has the original length of 90 cm. Spring A has constant 100 N/m, spring B has constant 200 N/m. The ratio of the change in length of spring A to the change in length of spring B is…
Known :
Constant of spring A (kA) = 100 N/m
Constant of spring B (kB) = 200 N/m
Force on spring A (FA) = F
Force on spring B (FB) = F
Wanted: ΔlA : ΔlB
Solution :
Hooke’s law formula :
Δl = F / k
Δl = the change in length, F = force, k = constant
The change in length of spring A :
ΔlA = FA / kA = F / 100
The change in length of spring B :
ΔlB = FB / kB = F / 200
The ratio of the change in length of spring A to the change in length of spring B :
ΔlA : ΔlB
F / 100 : F / 200
1 / 100 : 1 / 200
1 / 1 : 1 / 2
2 : 1
4. A nylon string with original length 20 cm, is pulled by a force of 10 N. The change in length of the string is 2 cm. Determine the magnitude of force if the change in length is 6 cm.
Known :
Force (F) = 10 N
The change in length (Δl) = 2 cm = 0.02 m
Wanted : the magnitude of force (F) if Δl = 0.06 m.
Solution :
Constant :
k = F / Δl
k = 10 / 0.02 = 500 N/m
The magnitude of force (F) if Δl = 0.06 m :
F = k x
F = (500)(0.06)
F = 30 N
[wpdm_package id=’689′]
