Electrostatic force – problems and solutions
1. If the static electric force is 144 N, what is the distance between both charges… (1 μC = 10-6 C and k = 9.109 N.m2.C-2)
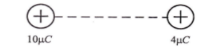
Known :
Electric force (F12) = 144 N
Charge 1 (q1) = 10 μC = 10 x 10-6 C
Charge 2 (q2) = 4 μC = 4 x 10-6 C
Constant (k) = 9 x 109 N.m2.C-2
C = Coulomb, N = Newton, m = meter
Wanted : Distance between both charges (r)
Solution :
The equation of Coulomb’s law :
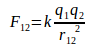
F = the static electric force, k = Coulomb’s constant, q = electric charge, r = distance between both charges
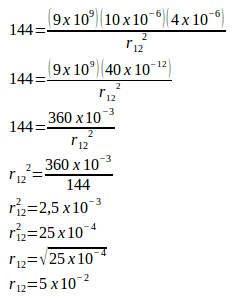
Distance between both charges (r) = 5 x 10-2 meter = 5 x 10-2 x 102 cm = 5 cm.
2. Two charges separated by a distance of r. If the static electric force is 3.6 N, what is the distance between both charges (1 μC = 10-6 C and k = 9.109 N.m2.C-2)

Known :
Electric force (F12) = 3.6 N
Charge 1 (q1) = 9 μC = 9 x 10-6 C
Charge 2 (q2) = 4 μC = 4 x 10-6 C
Coulomb’s constant (k) = 9 x 109 N.m2.C-2
C = Coulomb, N = Newton, m = meter
Wanted : Distance between both charges (r)
Solution :
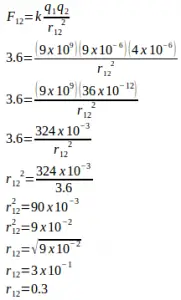
Distance between both charges (r) = 0.3 m = 0.3 x 100 cm = 30 cm.
3. Three point charges as shown in figure below. What is the magnitude of the static electric force at point A (k = 9.109 N.m2.C-2; 1 μ = 10-6)
Known :
Charge A (qA) = -2 μC = -2 x 10-6 C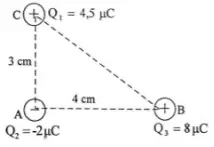
Charge B (qB) = 8 μC = 8 x 10-6 C
Charge C (qC) = 4,5 μC = 4,5 x 10-6 C
Coulomb‘s constant (k) = 9 x 109 N.m2.C-2
Distance between charge A and B (rAB) = 4 cm = 4 x 10-2 m
Distance between charge A and C (rAC) = 3 cm = 3 x 10-2 m
C = Coulomb, N = Newton, m = meter
Wanted : The static electric force at point A
Solution :
The equation of Coulomb’s law :
![]()
F = the static electric force, k = Coulomb‘s constant, q = electric charge, r = distance between both charges
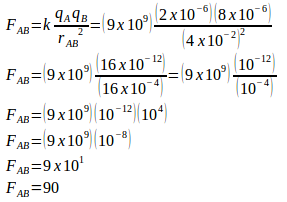
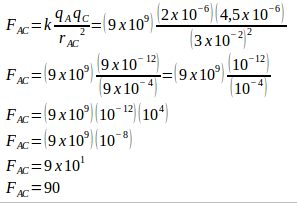
The static electric force at point A :
![]()
4. Three-point charges as shown in the figure below. What is the magnitude of Coulomb force experienced by Charge B (k = 9.109 N.m2.C-2; 1 μC = 10-6 C).
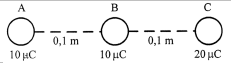
Known :
qA = 10 µC = 10 x 10-6 C = 10-5 Coulomb
qB = 10 µC = 10 x 10-6 = 10-5 Coulomb
qC = 20 µC = 20 x 10-6 = 2 x 10-5 Coulomb
rAB = 0.1 meter = 10-1 m
rBC = 0.1 meter = 10-1 m
k = 9 x 109 Nm2C−2
Wanted : Coulomb force experienced by Charge B
Solution :
There are two coulomb forces act on charge B, Coulomb force between charge A and B (FAB) and Coulomb force between charge B and C (FBC). Coulomb force experienced by charge B is net force of FAB and FBC.
Coulomb force between charge A and B :
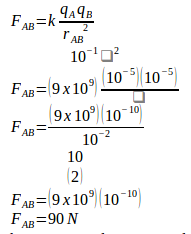
Charge A signed positive and charge B signed positive so that FAB points to charge C.
Coulomb force between charge B and C :
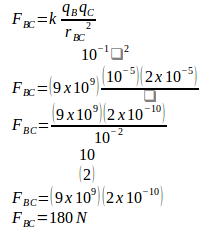
Charge B signed positive and charge C signed positive so that FBC points to charge A.
Coulomb force experienced by charge B :
FB = FBC – FAB = 180 – 90 = 90 N
Coulomb force experienced by charge B (FB) is 90 Newton. The direction of FB same as the direction of FBC points to charge A.
5. Determine the magnitude and direction of Coulomb force on charge B (k = 9 x 109 Nm2C−2, 1 μC = 10−6 C).
![]()
Known :
Charge A (qA) = +Q
Charge B (qB) = -2Q
Charge C (qC) = -Q
Distance between charge A and B (rAB) = r
Distance between charge B and C (rBC) = 2r
k = 9 x 109 Nm2C−2
Wanted : Magnitude and direction of Coulomb force on charge B
Solution :
Coulomb force between charge A and B :
![]()
Charge A positive and charge B negative so that the direction of FAB points to charge A.
Coulomb force between charge B and charge C :
![]()
Charge B is negative and charge C is negative so that the direction of FBC points to charge A.
Net force act on charge B :
F = FAB + FBC = 2 k Q2/r2 + 0.5 k Q2/r2 = 2.5 k Q2/r2 = 2.5 k Q2 r-2
Direction of force points to charge A or to leftward.
